This is Part I of the AI for PMs series. See AI for PMs - Part II on what to pay attention to when you start building an AI product.
Introduction
Today, AI / ML is at the cutting edge of technological innovation, impacting various sectors from healthcare to finance. Since OpenAI launched ChatGPT late last year, terms like LLMs, GPT, and GenAI have become buzzwords. Product hunt is filled with GenAI-based products, and the AI product landscape is growing exponentially 1. This article aims to clarify some misconceptions about AI and ML and what Product Managers need to know about them. While AI isn’t a cure-all, understanding its capabilities is key to competitive advantage.
It’s worth noting that the concept of AI is not new; it has ancient origins and has been part of human imagination for centuries, appearing in myths like the Biblical Golem and ancient automatons. The term ‘Artificial Intelligence’ itself was coined in 19562 and has been a subject of academic and cultural discussion ever since. With over 70 years of research history, AI and ML have been employed across various applications, but only in the last couple of decades, advancements in technology, including the explosion of internet usage and vast amounts of data, the availability of powerful cloud computing, as well as specialized GPUs and AI chipsets, have catalyzed the evolution and improvements of ML models.
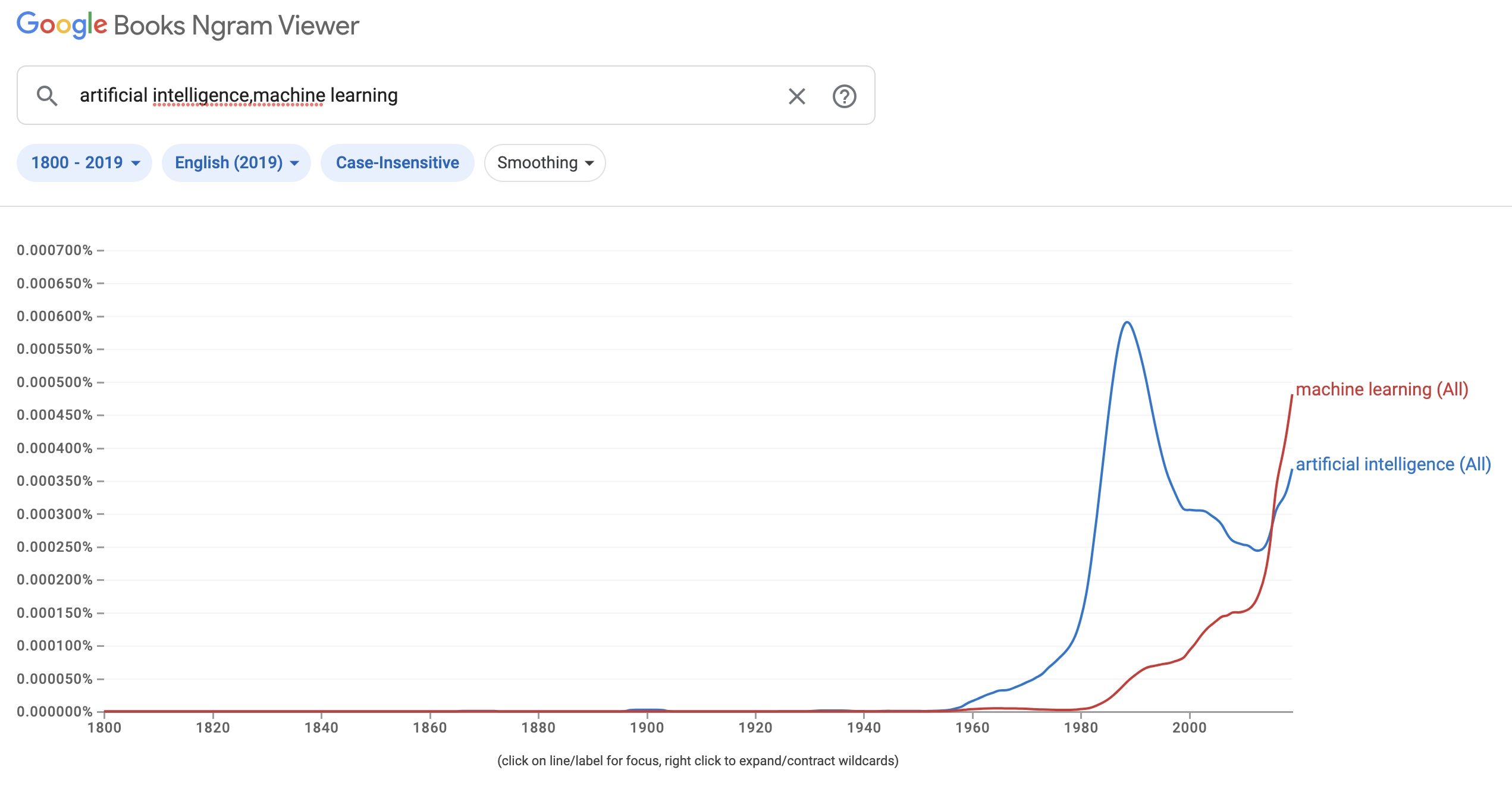
So, what is AI?
AI is an umbrella term covering various subfields, including Machine Learning (ML), Deep Learning, Generative AI (GenAI), and the ultimate goal, Artificial General Intelligence (AGI). Let’s go over the definitions:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Computer systems capable of performing tasks that typically require human intelligence.
- Machine Learning (ML)
- A subset of AI focused on developing algorithms that enable computers to make decisions or predictions.
- Deep Learning
- Specialized area within ML that utilizes multi-layer artificial neural networks to learn from large data sets.
- Generative AI (GenAI)
- Deep learning models capable of generating new data or content like images, music, video, or text.
- Artificial General Intelligence (AGI)
- The ultimate goal in the AI spectrum—a fully autonomous system capable of human-level intelligence across various tasks without requiring specialized programming.
Types of ML
There are four main types of ML models:
-
Supervised Learning: The model is trained on labelled data to make predictions or decisions.
Applications: Credit score applications, email spam detection, news topic classifications, and image recognition.
-
Unsupervised Learning: The model uses unlabeled data to find patterns or groupings.
Applications: Document clustering, customer segmentation based on buying behaviour, anomaly detection.
-
Semi-supervised Learning: The model uses both labelled and unlabeled data for training, often to improve performance.
Applications: Image recognition and other supervised learning applications.
-
Reinforcement Learning: The model learns to make decisions by interacting with an environment to achieve a goal or maximize some notion of cumulative reward.
Applications: Game playing, Autonomous vehicles.
Now, let’s dive into different AI/ML use cases.
AI/ML Use Cases
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) technologies are revolutionizing diverse industries. Here are some notable use cases and applications where AI/ML algorithms are making a difference:
- Credit Scoring & Anomaly Detection: Often use Supervised and Unsupervised Learning models.
- Chatbots & Customer Service & Customer Insights: Primarily rely on NLP, which can be built using Supervised Learning.
- Stock Trend Analysis: Typically use Time Series Algorithms, a form of Supervised Learning.
- Content Generation: Generative AI models to generate text, audio, code and video using form of Deep Learning that uses both Supervised and Unsupervised ML models,
- Supply Chain Optimization: Utilizes Optimization Algorithms, often built using Reinforcement Learning.
- Recommendation Systems: Generate individualized product, service, or content suggestions commonly employed in e-commerce, streaming services, and social media to boost user engagement. Both supervised and unsupervised models are being used.
Key Considerations Before Embarking on an AI Product Journey
Multiple critical factors have to be considered before you dive into developing an AI-powered product. Understanding these can be the difference between a successful launch and a missed opportunity.
Here are some pivotal elements to keep in mind:
Identifying AI Opportunities - Make sure the AI solution addresses a genuine customer need rather than merely finding an excuse to use an advanced AI model.
- Conduct market research to identify gaps or pain points that AI can solve.
- Validate the idea with stakeholders and potential users.
- “Fall in love with the problem and not with the solution” - Don’t implement AI for the sake of adding AI to your product.
Finding the Right Partner - Developing AI/ML applications requires specialized expertise. Finding the right partner is crucial whether you look inside your organization or seek an external vendor.
- Evaluate potential partners based on their previous work and their expertise in the domain.
- Ensure that the partner aligns with your organization’s culture and goals.
Data Is Key - If you have to build your model, the right data and its quality would be of the utmost importance. Data is the backbone of any AI project and is crucial for training models. In many cases, continuous training might also be necessary to adapt to new data patterns.
- Ensure you have access to the right amount of a high-quality and relevant data.
- Consider the ethical implications and legal requirements associated with data collection and usage, more about it in my next post.
AI-Application Fit - Understanding the pros and cons of various AI and ML techniques is essential. Discuss with your partner to choose the most appropriate algorithm for your specific problem and use case.
- Perform a feasibility analysis to identify the most effective AI or ML techniques.
- Keep scalability, cost, and performance in mind when choosing algorithms.
Resource Allocation - Be clear about the human and computational resources required to bring your AI project to life.
- Create a detailed project timeline and budget.
- Consider the long-term maintenance costs of the AI system.
Conclusion
AI offers numerous opportunities for innovation in product management. Awareness of its possibilities can significantly benefit your role as a Product Manager. Be curious, follow AI trends, learn and create products that solve customer pain points and delight customers with the help of AI/ML features and algorithms.
Check AI for PMs - Part 2 for tips on what to pay attention to when building AI-based products.
Additional Resources
This article is just a primer to provide some knowledge and kick off your curiosity to learn more. Here is a short list of articles, courses and books to keep you going:
- AI for Everyone (Coursera)
- Becoming an AI-First Product Leader (LinkedIn Learning)
- Artificial Intelligence for Business Leaders (LinkedIn Learning)
- AI Product Management Specialization (Coursera)
- Generative AI Landscape (Sequoia ; Antler)
- A collection of a real-world ML applications
- Prompt Engineering Guide: Promptingguide.ai
- Keep up with the latest news in the AI space with TLDR AI
-
AI and GenAI landscape is enormous. Here are some examples: Sequoia GenAI, DataCamp ↩
-
The field of AI research was founded at a workshop held on the campus of Dartmouth College, USA during the summer of 1956. ↩




Comments